
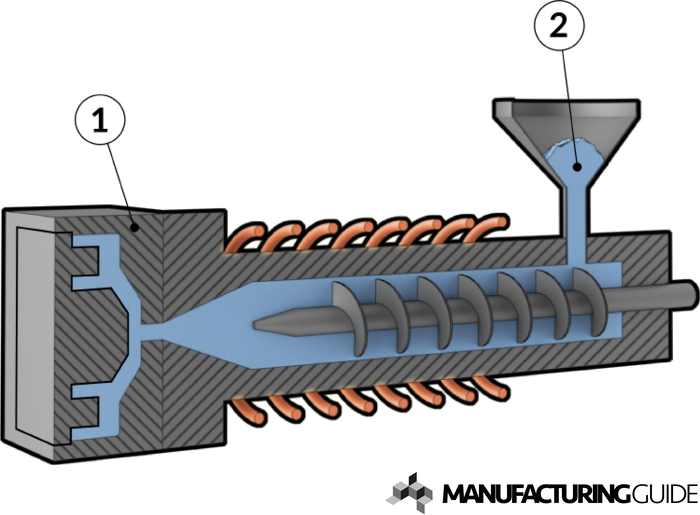
Metal and ceramic injection molding provide better dimensional and productivity limits of isostatic pressing and slip casting. Metal and ceramic injection molding technology offers the design flexibility for unlimited choice of material offered by powder metallurgy (powdered metal and ceramic). Together these two technologies are popularly known as powder injection molding (PIM). There are physical, chemical, and electrical methods for producing the metal powders used in MIM, but we use water atomization, a process in which molten metal is reduced to fine particles by blasting it with water.Metal injection molding (MIM) and ceramic injection molding (CIM) are advanced manufacturing technology used in manufacturing of complex, precision, net shape components from metal and ceramic powder respectively. Process parts made from titanium and titanium alloys using MIM.Įpson Atmix manufactures its own metal powders. Epson Atmix is differentiated by its ability to sinter workpieces to a density of 99.5%, stably produce very small parts with complex shapes in high volumes, and We are able to manufacture high-quality MIM parts because we have expertise in the entire production process, from the manufacture of our own powders to the molding MIM is a relatively new processing method that takes time to learn, but Epson Atmix has been engaged in the MIM business since the 1980s when the technology was introduced However, MIM has an advantage over 3D printing in that it lends itselfīetter to volume production, is more flexible in terms of the materials that can be used, and requires less post-processing. Therefore, there are cases where multiple parts that were conventionally manufactured by milling or other machining operations can be metal injectionģD printing is one method that can be used to create three-dimensional shapes using metal powder. As long as the shape can be achieved by injection molding, thereĪre not many limitations. MIM allows you to create three-dimensional shapes that cannot be achieved by machining or sheet metal working.



If high dimensional accuracy is required or if additional processing such as screw tapping is required, sizing (coining) or machining are performed. Sizing, machining (secondary processing), and surface finishing Epson Atmix uses its own metal powder and MIM sintering technology to achieve a sintered density that was not possible with conventional MIM. Sintered workpieces are called silver parts. The cubic volume of sintered parts will be reduced by an amount corresponding to the amount of binder lost. The degreased brown parts are heated and sintered in a sintering furnace. The degreasing process must be carefully controlled because if degreasing is not performed correctly, grease left behind will be present as carbon during sintering, affecting the composition of the metal after sintering. Care must be used in degreasing because the wax components escape from between the particles, which can lead to deformation and cracking. Workpieces that have been degreased are called brown parts. (3) Catalytic degreasing, in which catalytic gas and heat are used to achieve degreasing


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
